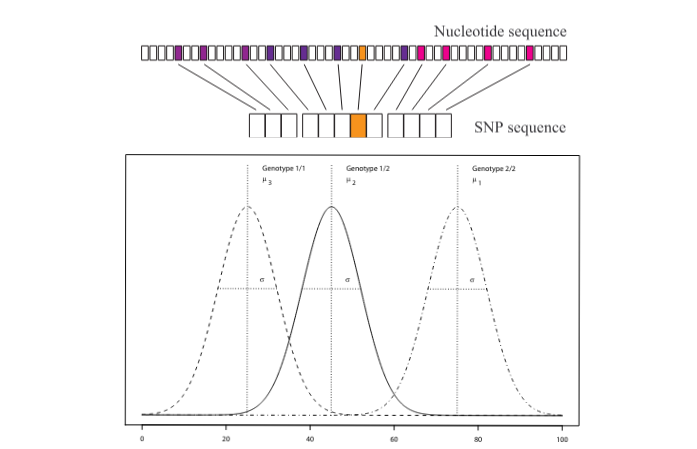
SNaP stands as a robust simulation program designed for the analysis of haplotypic and genotypic data related to single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
It operates on the assumption that SNPs occur in one or more independent haplotype blocks, i.e., genomic regions that are not correlated with each other (no linkage disequilibrium).
Each of these blocks may harbor a causative SNP that can influence an optional phenotypic expression. This expression can manifest as either a qualitative trait (affection status) or a quantitative trait (QT). These features find application in diverse scenarios, ranging from the exploration of haplotype-based analyses to QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) analyses.